NEW QUESTION 80
DRAG DROP
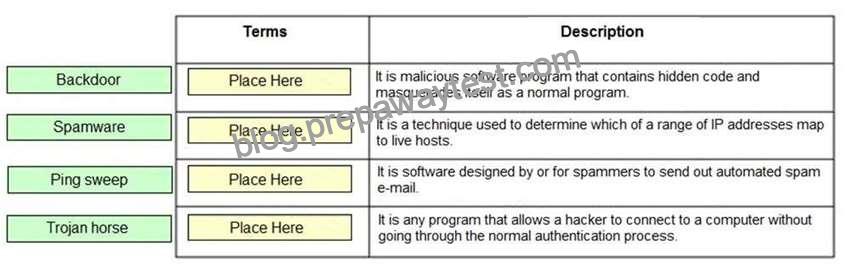
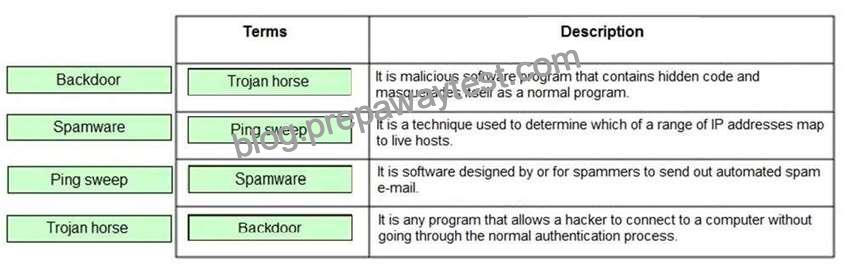
Drag and drop the terms to match with their descriptions.
Select and Place:
Explanation:
Following are the terms with their descriptions:

A Trojan horse is a malicious software program that contains hidden code and masquerades itself as a normal
program. When a Trojan horse program is run, its hidden code runs to destroy or scramble data on the hard
disk. An example of a Trojan horse is a program that masquerades as a computer logon to retrieve user
names and password information. The developer of a Trojan horse can use this information later to gain
unauthorized access to computers. Trojan horses are normally spread by e-mail attachments. Ping sweep is a
technique used to determine which of a range of IP addresses map to live hosts. It consists of ICMP ECHO
requests sent to multiple hosts. If a given address is live, it will return an ICMP ECHO reply. A ping is often
used to check that a network device is functioning. To disable ping sweeps on a network, administrators can
block ICMP ECHO requests from outside sources. However, ICMP TIMESTAMP and ICMP INFO can be used
in a similar manner. Spamware is software designed by or for spammers to send out automated spam e-mail.
Spamware is used to search for e-mail addresses to build lists of e-mail addresses to be used either for
spamming directly or to be sold to spammers. The spamware package also includes an e-mail harvesting tool.
A backdoor is any program that allows a hacker to connect to a computer without going through the normal
authentication process. The main advantage of this type of attack is that the network traffic moves from inside
a network to the hacker’s computer. The traffic moving from inside a network to the outside world is typically
the least restrictive, as companies are more concerned about what comes into a network, rather than what
leaves it. It, therefore, becomes hard to detect backdoors.
